What is genital wart ?
 Genital warts are one of the most common types of sexually transmitted infections. It occurs when a virus called HPV (Human Papilloma Virus) infects a person.
Genital warts are one of the most common types of sexually transmitted infections. It occurs when a virus called HPV (Human Papilloma Virus) infects a person.
Almost all sexually active people encounter this virus at some time in their lives. This virus causes the formation of genital warts in both men and women, while in women it can also cause cervical (cervix) cancer. Warts affect the moist areas of the genital area. A genital wart may be too small to be seen by the eye, or it may also appear in larger shapes, such as small bumps or sunflowers.
What are the symptoms of genital warts?
In women, warts usually occur on the lips of the vagina, in the area between the anus and vagina, in the anal canal, on the walls of the vagina and on the cervix (cervix). Decubitus. In men, it can be observed in the penis, scrotum (testicular bag) and anus. People who have oral sexual contact with a person infected with HPV may experience the formation of warts on the mouth, tongue and throat.
Vaginal discharge, itching, burning sensation and bleeding along with warts in the genital areas are among the symptoms that are usually seen together. Decongestants are the most common causes of genital warts.
Why does genital wart occur?
A wart is formed when a virus called HPV infects a person. There are more than 40 subspecies of HPV that affect the genital area. Only a few of these subspecies cause the formation of warts. HPV is a virus that spreads through contact. A person infected with HPV may not show any symptoms and may transmit this virus to his partner sexually. The virus disappears spontaneously over time without showing any symptoms in most people. However, it can lead to the formation of warts in some people. In order for the person carrying the virus to infect the opposite party, it is enough for the sexual areas to come into contact. Since it is a virus of small size, it can easily enter the body by passing through small abrasions and cracks on the skin.
What are the risk factors for genital warts?
The vast majority of sexually active individuals become infected with the HPV virus at least once in their lives. Those infected with the HPV subtype that causes the formation of warts can also get genital warts. Some risk factors increase the likelihood of encountering HPV. These:
* Unprotected sexual intercourse with multiple partners,
• Having a sexually transmitted disease other than genital warts,
* Becoming sexually active at an early age,
• It can be counted as having diseases that suppress the immune system or receiving such treatments (such as chemotherapy).
What diseases does HPV infection lead to other than genital warts?
People infected with HPV usually get rid of this virus within a few years. However, the virus can continue to exist in the body, causing various problems. Some subspecies of HPV cause genital warts, while some subspecies also lead to the formation of cancer. Cervical (cervix), anus, mouth, penis cancers are cancers that are closely related to HPV infection. Cervical cancer, especially in women, is highly associated with HPV. Women should be screened for cervical cancer by performing Pap smear test at December intervals after the age of 30. This screening test is very important for early detection and treatment of cervical cancer.
Does genital warts cause problems during pregnancy?
It is a rare occurrence for genital warts to cause an October problem throughout pregnancy. Although it is not common, warts can grow and make it difficult to urinate. Warts located on the vaginal wall can prevent the vaginal tissues from stretching during childbirth. Warts located on the lips of the vagina can bleed due to excessive enlargement during childbirth. Although it is a fairly rare condition, the formation of warts on the throat of babies born to a mother with genital warts can be observed. These warts may need to be surgically removed in order to prevent the baby from blocking the airway.
Is it possible to prevent the formation of genital warts?
There are vaccines developed against HPV, which plays a role in the formation of various cancers, especially genital warts and cervical cancer. Just as there is a vaccine that protects only against HPV subtypes that cause cancer, there are vaccines that also protect against HPV subtypes that cause genital warts to form next to cancer. These vaccinations can be given to everyone by the age of 45. However, vaccination before the start of active sex life provides more effective protection. It is recommended that boys and girls get the HPV vaccine after the age of 9. In this way, they are less likely to develop diseases such as genital warts and cervical, penile cancer in the future. In addition, the use of condoms that prevent skin contact during sexual intercourse is also a prevention method that reduces the risk of genital warts.
How is genital wart diagnosed?
The diagnosis is usually made by the appearance of warts. However, in some cases, a biopsy may be required. In addition to these, the presence of risk factors is investigated by asking the patient about his sexual history. In women, a pelvic examination can also be performed, as warts can also appear on the deeper parts of the genital organs. During the examination, an acidic solution can be applied to the genital area to see the warts more easily. In addition, the doctor can also give the patient a Pap test. While this test is being performed, the doctor inserts an instrument called a speculum into the patient's vagina. In this way, the tissues between the vagina and the uterus are examined more Decently. When examining with a speculum, a tissue sample is also taken with the help of a brush over the cervix (cervix). The cells in the tissue sample are evaluated for the presence of HPV by special methods. In case abnormal cells (HPV-infected cells) are detected as a result of the test, further examination is performed using methods that allow a more detailed examination, such as colposcopy. If cervical cancer is suspected, an HPV DNA test can be performed to investigate the presence of genetic material belonging to HPV in the body. All these diagnostic methods are important methods that can be used to diagnose diseases such as genital warts, cervical cancer associated with HPV.
How is genital wart treatment?
The main goal in the treatment of genital warts is to eliminate the discomfort caused by the wart and reduce the size of the wart. People who do not experience discomfort from warts may not need treatment. Since there is no effective treatment for HPV, which causes warts, a person who has received the virus into his body may experience attacks of warts from time to time. The probability of recurrence of the disease after treatment in patients is quite high. The most commonly used method of treatment is the use of cream. Types of genital wart cream, which contain different active ingredients, exert their effect in different ways. Creams containing imiquimod strengthen the immune system, allowing this system to fight warts more strongly. After the cream is applied to the genital area, it is recommended not to have sexual intercourse for a certain period of time. The most common side effect is that it causes redness on the skin. Creams containing podophilin and podophilox can also be used in the treatment. These creams should not be applied to the internal areas of the genital organs and are not recommended for use during pregnancy. Other types of creams can also be used to treat genital warts. Your doctor will prescribe the most suitable cream for you and demand that you use it regularly. With cream treatment, it is aimed to reduce uncomfortable conditions such as itching, redness, burning caused by the wart.
Surgical methods can be used in treatment for reasons such as the inability to treat genital warts with cream, to the extent that they can cause problems during childbirth in pregnant women. Warts can be eliminated by burning with laser, freezing, surgical incision or electrocautery by burning with the help of electric current.
If you have symptoms of genital warts and are uncomfortable with this condition, it will be useful to contact an experienced gynecologist at an experienced center. It is very important to get an expert opinion on issues such as different treatment options and diseases that may be seen with warts. We wish you healthy days.
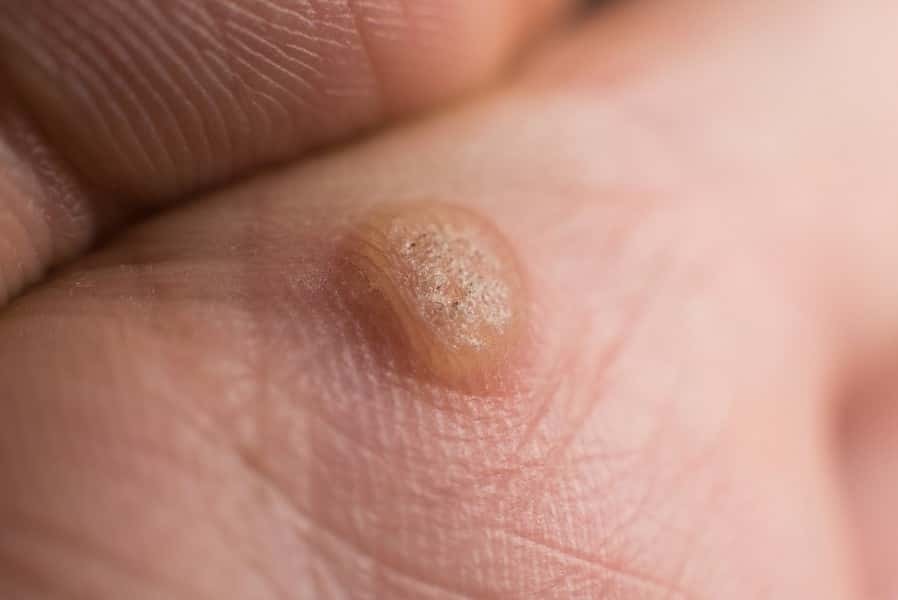 Genital warts are one of the most common types of sexually transmitted infections. It occurs when a virus called HPV (Human Papilloma Virus) infects a person.
Genital warts are one of the most common types of sexually transmitted infections. It occurs when a virus called HPV (Human Papilloma Virus) infects a person.