What Is Good for a Burn Scar?
 Learn more about Burn scar
Learn more about Burn scar
What Is Good for a Burn Scar?
Sometimes we can burn our hands and arms while making tea, sometimes while cooking in the oven, sometimes while ironing. Burns are the most common household accidents. Burns are serious damage to the affected skin layers in that area as a result of an external factor. This skin damage usually occurs after contact with heat. Sometimes this is not a heat contact, it can also be the result of chemical or radiation.
Burns caused by dry heat (such as fire or iron) and burns caused by wet (such as scalding, hot water or steam) are common. Burns are one of the reasons why children are also taken to the emergency room. Children, the disabled and the elderly are most at risk of burns. These people can burn by touching the hot pot or boiling water. Hot tea, coffee or milk burns, which we call scalding burns, are common in children, while lighter, firecracker, match and sun burns are more common in young people. Other causes of burns are as follows:
Friction Burns: These are burns that occur as a result of rubbing a hard object against your skin. This may be due to wear or heat. Motorcycle and bicycle accidents are examples of these.
Cold Burns: Cold burns, also known as frostbite, occur with prolonged exposure to cold. Ice applications can also sometimes cause cold burns.
Thermal Burns: Occurs by touching a hot object. Too hot metals, boiling liquids and flames are the cause of thermal burns.
Radiation Burns: X-ray or radiation therapy rays received as part of cancer treatments can cause these burns.
Chemical Burns: Chemical burns can occur due to strong acids, solvents or detergents.
Electric Burns: These burns can occur if they come into contact with an electric current.
Degrees of Burns
The pain felt and the degree of burn are not always in the same ratio. Even very serious burns can sometimes be painless. The factors that determine the severity of the burn are:
Depth
Prevalence
Area
Risk of infection
Age
Harm seen through breathing
Existing diseases
Burns caused by exposure to heat, chemicals, sunlight, electricity, radiation are graded according to their depth and the amount affected. The higher the degree of burn, the more severe the burn. The degrees of burns are listed as follows:
First Degree Burns: Occur in the upper layer of the skin (epidermis). Redness, pain, edema may occur in the burned area. No blistering is seen. It heals in about 48 hours.
Second Degree Burns: Occur in the upper and lower layers of the skin (dermis). Blisters filled with water (bullae), swelling occur on the skin and are painful. It heals with the self-renewal of the skin. If you have a superficial second-degree burn, it means that only part of the dermis is damaged. There may be no scars. If it is deeper, it can leave scars and there will be a permanent change in the color of the skin.
Third Degree Burns: All layers of the skin and subcutaneous fatty tissue are affected. 3. a severe burn also destroys the hair follicles and sweat glands. The skin may become charred. Most of the time there is no pain, as the nerves are damaged. It destroys the epidermis and dermis.
Fourth Degree Burns: These burns are the deepest and most severe burns. They are life-threatening. It can damage all layers of the skin, bones, November muscles and tendons.
Sometimes the degrees of burns can vary. This condition can be seen if your skin damage continues to spread and your wounds deepen. Depending on the degree of the burn, sometimes people can go into shock. Symptoms of shock include pale and clammy skin, weakness, bluish lips and nails, clou Decency of consciousness.
What's Good for a Burn?
Some burns are minor injuries that you can treat at home. But some November burns can cause permanent damage to your skin, muscles and bones and require long-term medical treatment. Burns can bring with them many complications, including infection, bone and joint problems. Therefore, doctor's intervention is important in burns. Especially with third-degree burns, you should go to the emergency room. For first responders in burns, the following can be applied:
The person should be removed from the cause of the burn. If the cause of the burn is electrical, make sure that the electrical power is turned off.
It should be checked whether the person is breathing. If he is not breathing, artificial respiration should be performed.
If there are products such as jewelry and belts on the person, they should be removed.
The burn area can be kept in non-cold water for a maximum of 15 minutes.
The burned area should be covered with a clean, cold cloth or wrapped with a slightly wet bandage. Jul.
If possible, the burned area should be kept above the level of the heart.
One should be wary of shock symptoms such as fainting, dizziness, pale skin and shallow breathing. If there is one of them, the feet and legs should be raised up without moving the body. If vomiting occurs, the person should be turned on his side due to suffocation.
Do not try to take off your clothes, cut them off so that the clothes do not stick to the burn.
Be careful not to get direct sunlight.
What to Rub into the Burn?
Creams containing aloe vera or antibiotic burn ointments may be good for a first-degree burn. Second degree burns may require dressing with special burn wound dressings. For other burns, the intervention should be carried out directly in the hospital. Products such as any oil, yogurt, toothpaste should never be applied to the burned area. An excessively cold compress should not be applied to the burn or ice should not be put on it. Ice can worsen the damage. Cotton should not be put on burn wounds. Because the fibers in the cotton can stick to the wound. This, in turn, can increase the risk of infection. Avoid bursting bubbles that form on burns. Because blasting these wounds can increase the risk of infection.
When Should I Go to the Doctor For a Burn?
In case of electrical, chemical or flame burns, the patient should definitely go to the hospital. If the burn area is large, the patient should consult a doctor if there are burns to the hands, face, genitals. If the large area is burned again, 2. in case of burns seen in infants and children of degree and above, the family should definitely contact the hospital. In addition, if the burn becomes painful and smelly, if a high temperature is felt October, if more than 5 years have passed since the last tetanus vaccine, you should go to the emergency room.
Burn Treatment
1. a degree burn can heal with home treatment. But 3. and 4. severe burns are injuries that need urgent intervention by a doctor. If the second-degree burns are also deep, the doctor's intervention is inevitable. In case of second degree burns, dressing should be done with burn wound care cloths recommended by the doctor. 3. and 4. in case of severe burns, intranevous antibiotics are given to prevent infection, while IV fluids are used to replace the lost fluid.
Burn pains can be intense and last a long time. It is important to clean the wounds and make dressings regularly. 3. and 4. severe burns may require intensive burn treatment. The following complications can develop due to a burn:
Sepsis
Hypovolemia
Hypothermia
Respiratory problems caused by smoke or hot air
Bone and joint problems
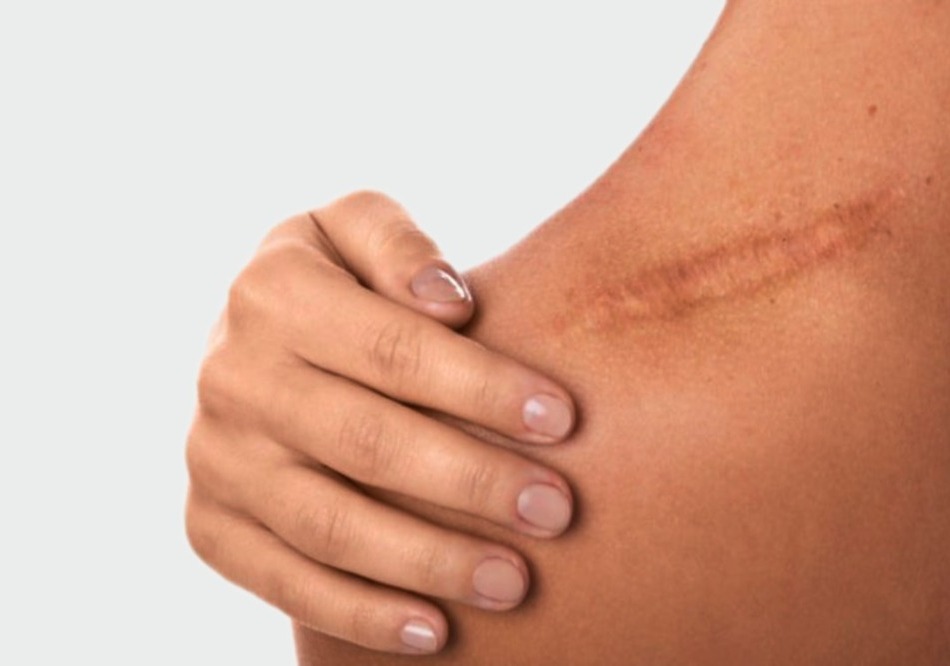
How Does the Burn Scar Pass?
Medications that should be used in burn treatments should not be left unfinished. Sometimes 2. a degree burn can also leave scars. In the case of third and fourth degree burns, scarring is inevitable. There are special gels for burn scars. Again, after the wounds have healed, creams with St. John's wort oil and ingredients for the burn scar can also benefit. The burn mark must necessarily be protected from the sun's rays.
Precautions That Can Be Taken Against Burns at Home
When there are utensils such as pots, pans, teapots, coffee pots on the January, turn their handles inward against bumps.
If there are babies or children in the house, keep them away from the kitchen while cooking. Also, keep away from any devices that may get hot. Close the covers of electrical outlets.
Have a fire extinguisher tube on each floor of your home. Make sure that the fire extinguishing devices are constantly working.
Do not smoke in bed.
Make sure that the water temperature in the house is always below 120 degrees. First of all, check the temperature of the water before bathing your baby.
If your car is parked in the sun, make sure that all the belt buckles are warmed up before putting your baby in the seat again.
Wear glasses and a mask when working with chemicals. Put them in places where children cannot lie down.
Do not place electrical appliances near water. Unplug it when not in use and put it in safe places away from children.
 Learn more about Burn scar
Learn more about Burn scar